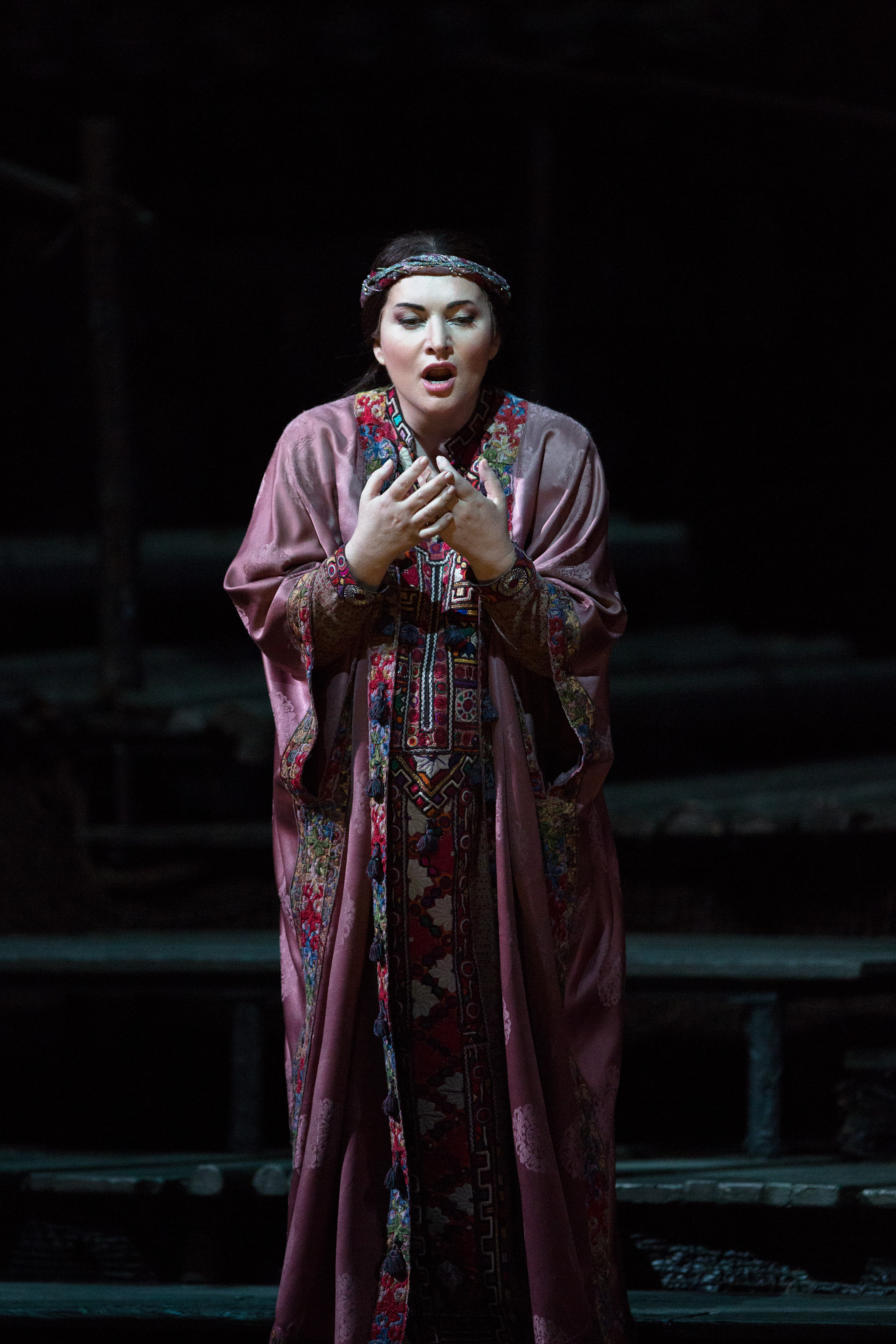
Lately the idea of rejuvenation intrigues. As I wrote in the introduction to a recent post detailing a newcomer’s thoughts on Bizet’s Carmen and the opera-going experience itself, ideas related to perception, exposure, cynicism, approach, and re-approach have been more active than usual. There is a certain value to seeing something so famous with new eyes (and ears), particularly given the grim realities pandemic continues to present. To make the effort to re-appreciate opera anew is to confront old questions with a new awareness. What is opera – is it only singing? Is it also scoring? Is it theatre? Is it design? Is it sitting in the dark, in silence, with strangers? Is it some alchemical combination of these things? Rediscovery demands return – and not only in a literal sense – and return demands simplicity. To return to an art form one once loved experiencing live is to take off the over-tight bustier and flesh-gouging garters, to peel off eyelashes and unpin hair, to throw dress, fan, and shoes across the room and not worry what anyone thinks; it is to see and feel opera naked, unadorned, free from pretense, bare-faced. There is a freedom in that – for voice, score and theatre, as much as for the curiosity which must fuel them all.
Indeed regular reassessments are needed, for audiences and industry – to search for and find the freedom such curiosity might grant; to embrace the responsibility which is inherent to that (and all) freedom; to constantly bring the clarity such freedom grants to an art form which can (does) often fall into the traps of obfuscation, disorder, decay, and intransigence. Thus is the work of some artists who work with and around houses all the more important; often their work is what opens the door – to freedom, return, simplicity. They aren’t so much working on the peripheries as within the very essence, keeping that sense of curiosity ever alive. I have admired the work of Monika Rittershaus for many years; her stage photography graces many a program book and web page. She has shot productions for Los Angeles Opera, Staatsoper Hamburg, Bayerische Staatsoper, Komische Oper Berlin, Staatsoper Unter den Linden (Berlin), Festival d’Aix-en-Provence, Teatro Real Madrid, and Opernhaus Zürich, to name just a few. Her work is a quietly powerful integration of dramaturgical and humanistic, revealing opera as an art form comprised of sounds, sights, and souls. Born in Wuppertal, the busy stage photographer first studied philosophy, German language and literature, and art history. Finding inspiration in the works of choreographer Pina Bausch, she went on to study photography in Dortmund, which led to commissions in Vienna, Basel, Bregenz, Hamburg and Stuttgart. Rittershaus has been a freelance theatre and concert photographer since 1992.
 The scene and the unseen: Oper in Bildern – Fotografien von Monika Rittershaus (arnoldsche) is a new book filled with imagery shot between a variety of locales between 2006 and 2022. The work, edited by Iris Maria vom Hof, demonstrates a breadth of modern directorial vision, with shots of the stagings of Christof Loy, Claus Guth, Christoph Marthaler, Patrice Chéreau, Hans Neuenfels, Calixto Bieito, Silvia Costa, Romeo Castellucci, Andreas Homoki, Nadja Loschky, Mariame Clément, Dmitri Tcherniakov, Kirill Serebrennikov, and Tobias Kratzer, among many more. Stagings by Achim Freyer, whom Rittershaus names in our exchange (below) and Barrie Kosky, who writes an introduction, are also featured. The many hours spent pouring through the book’s thick pages bring memories and a feeling that perhaps operatic rejuvenation is not as far as one may think; I’ve seen some of the productions featured in this book, and these photos don’t make me nostalgic so much as clear-eyed. Kosky writes that Rittershaus “seems to sense the inner world of a moment and to know at exactly the right moment when to click her camera. There is an extraordinary intuition at work here. Perceptive, refined, and sophisticated.[…] She doesn’t document the moment. She x-rays the moment.”
The scene and the unseen: Oper in Bildern – Fotografien von Monika Rittershaus (arnoldsche) is a new book filled with imagery shot between a variety of locales between 2006 and 2022. The work, edited by Iris Maria vom Hof, demonstrates a breadth of modern directorial vision, with shots of the stagings of Christof Loy, Claus Guth, Christoph Marthaler, Patrice Chéreau, Hans Neuenfels, Calixto Bieito, Silvia Costa, Romeo Castellucci, Andreas Homoki, Nadja Loschky, Mariame Clément, Dmitri Tcherniakov, Kirill Serebrennikov, and Tobias Kratzer, among many more. Stagings by Achim Freyer, whom Rittershaus names in our exchange (below) and Barrie Kosky, who writes an introduction, are also featured. The many hours spent pouring through the book’s thick pages bring memories and a feeling that perhaps operatic rejuvenation is not as far as one may think; I’ve seen some of the productions featured in this book, and these photos don’t make me nostalgic so much as clear-eyed. Kosky writes that Rittershaus “seems to sense the inner world of a moment and to know at exactly the right moment when to click her camera. There is an extraordinary intuition at work here. Perceptive, refined, and sophisticated.[…] She doesn’t document the moment. She x-rays the moment.”
Rittershaus and I recently enjoyed an email exchange following an autumn in which she photographed the new production of Wagner’s Ring Cycle by Dmitri Tcherniakov for Staatsoper Unter den Linden (Berlin).
Monika Rittershaus
How much of a prior working relationship do you have (or require) with a director in order to photograph their production?
There is an initial collaboration with each directing team. Before I go to the rehearsal, I read or listen to the piece to be photographed. For world premieres, I ask for any materials that are already accessible. I watch the first rehearsals without a camera to understand, as much as possible, how a production is ‘built’ and what the specific concern of the team might be with this work. If I can work with a team more often, understanding becomes greater and mutual trust stronger. So an intensive working relationship is very nice for me in any case, even if it doesn’t basically result in a shorthand language, because I engage with each production anew. Barrie Kosky in particular is constantly inventing new languages for his productions. With him, there is a kind of intuitive and playful agreement for me.
How easy (or challenging) is it to integrate your own artistry with that which is being presented visually and sonically?
When I photograph a production, I try to translate the artistic template into my images as sensitively and accurately as possible. If successful, it does not remain an objective image. My desire is to show the sensitive structure on stage, in its complexity, to capture a moment that, in the best moments, flashes something that escapes the eye. What I mean by “sensitive structure” is this: in an opera performance, very many processes and aspects intertwine and depend on each other. Singers, conductor, orchestra, stage, stage management, props, lighting, costumes, transformations… everything should ‘breathe’ with each other; then a special magic is created, which is very sensitive, and fleeting, because it is in constant movement.
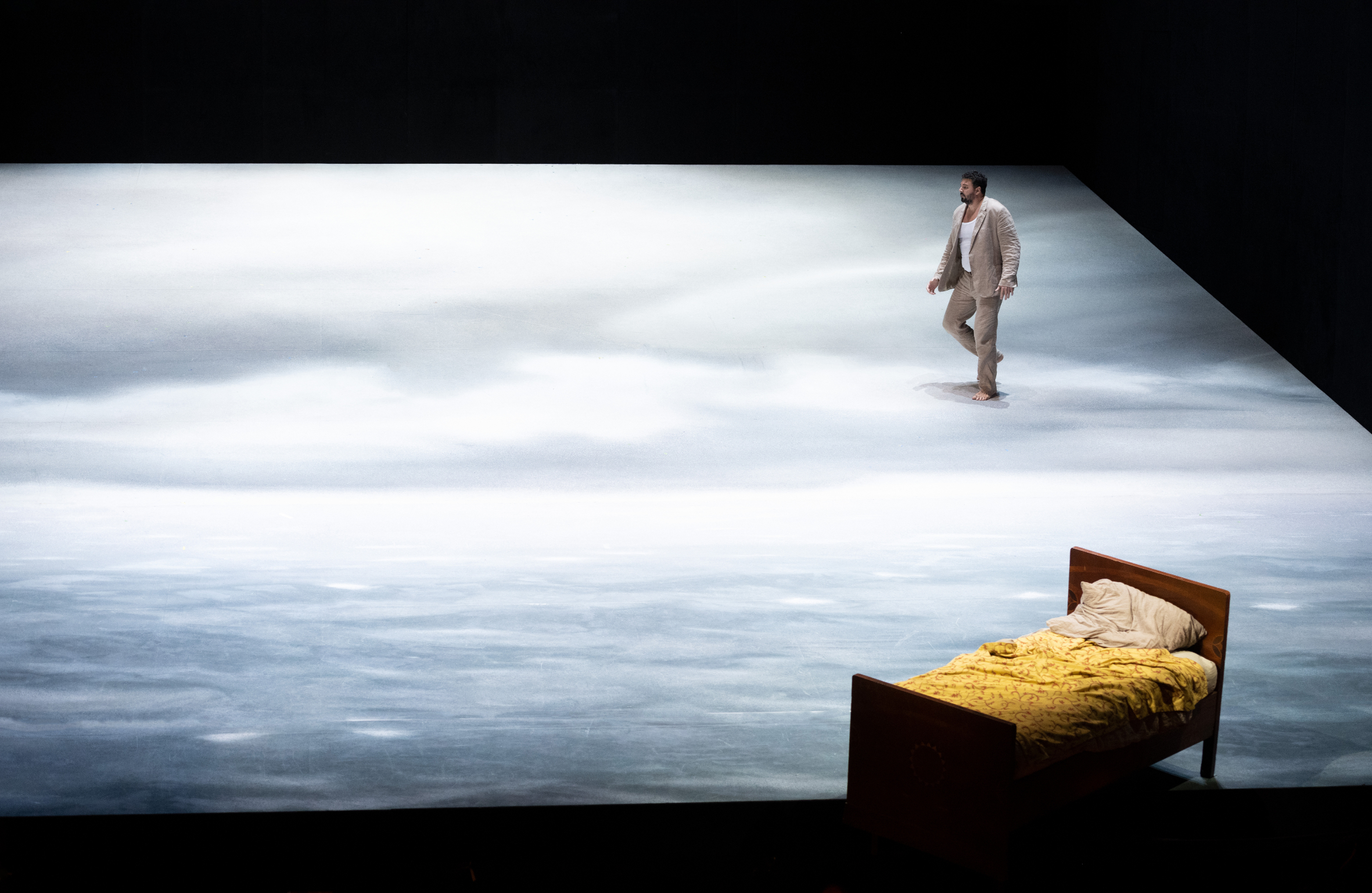

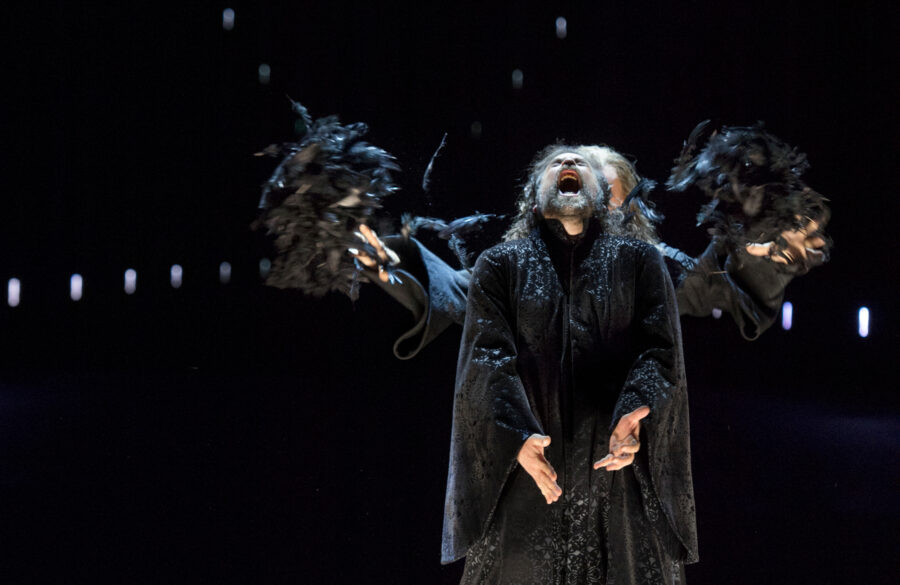
Eric Cutler as Peter Grimes in a scene from Theater an der Wien’s staging of Britten’s opera, by director Christoph Loy, 2021. Photo: Monika Rittershaus
What is the role of the voice in your work? Is there one?
The voice in the literal sense, does not really play a role in my work. I listen very carefully to every voice on stage and am touched by what singing people can tell through their voices. However, I tend not to try to show the physical act of singing.
How has your idea of visual expression changed through all the operas you have photographed?
There are productions that reach me particularly deeply and teams that expand my perspective and visual approach through their work – this doesn’t necessarily have to do with a specific work, although there have been incisive experiences in this regard as well.
I began my path in opera with Achim Freyer. He is a strongly image-based artist from whom I have learned a great deal and may still learn. He has been very supportive of my particular preference for compositions of people in space and the amplification of content that comes with it.
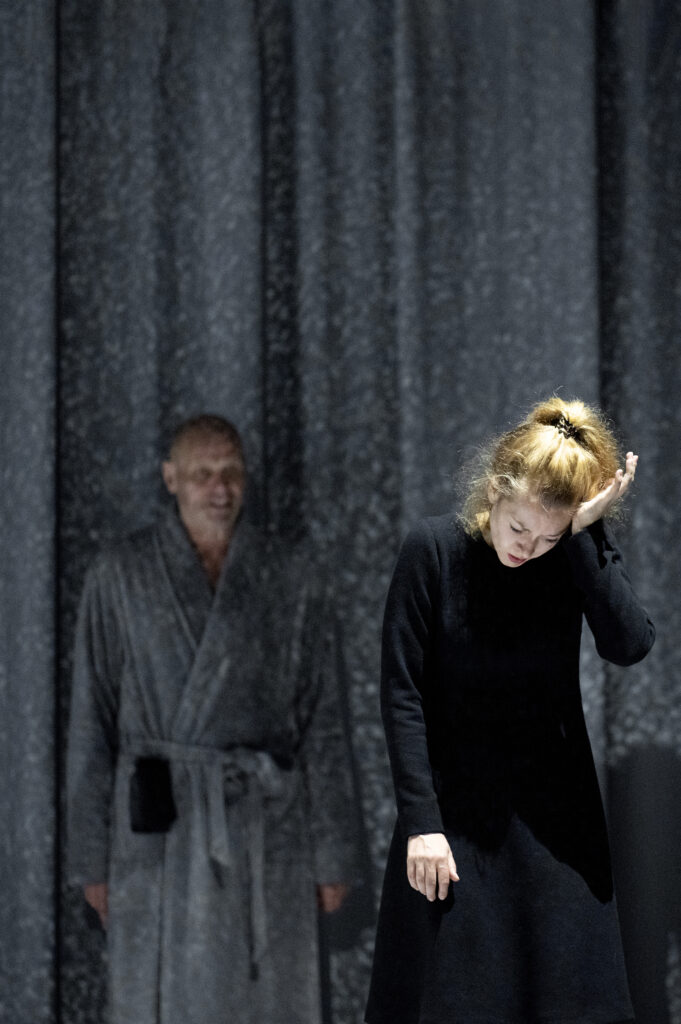

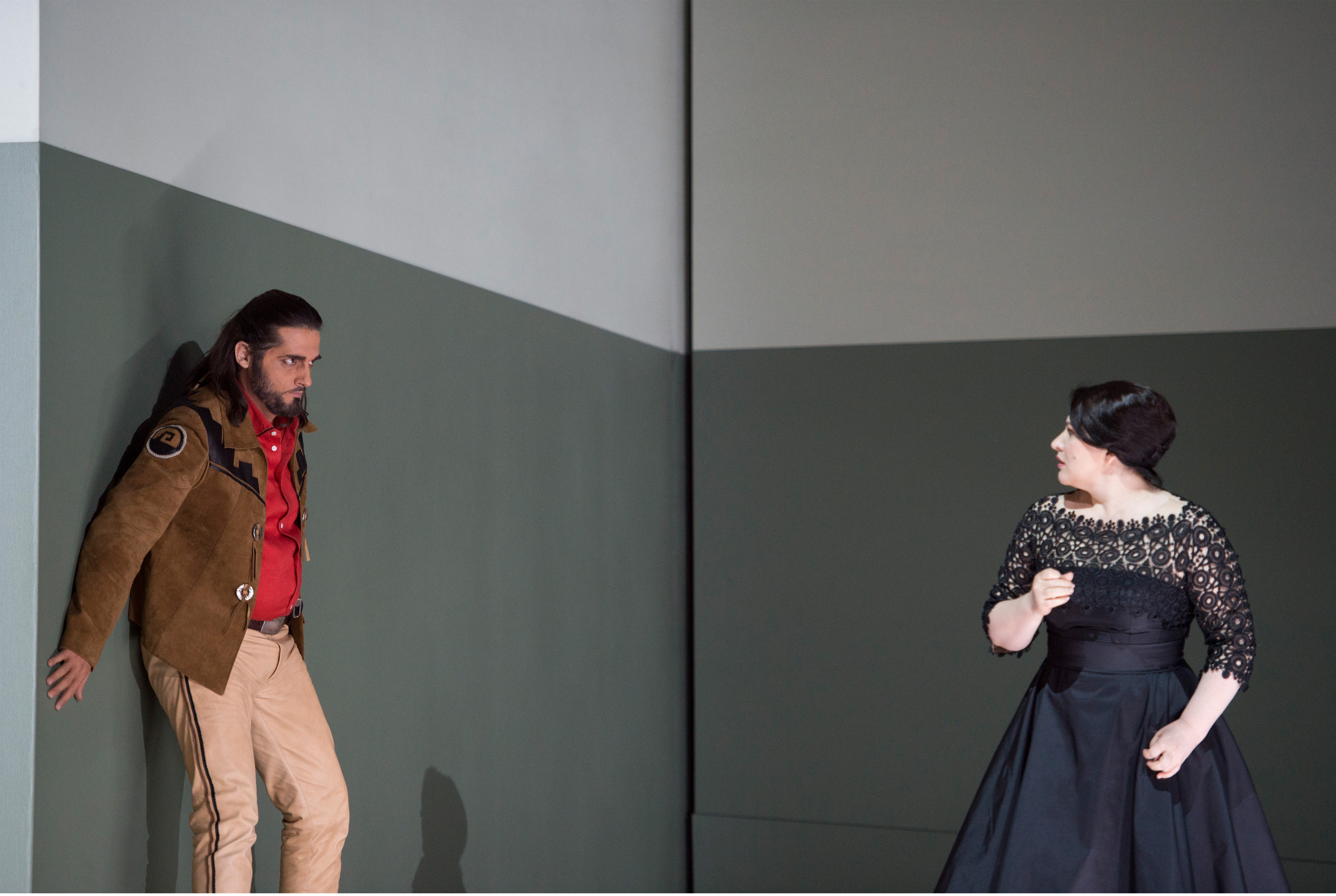
Bo Skovhus (L), Vera-Lotte Boecker (R). A scene from Bayerische Staatsoper’s Bluthaus, by Georg Friedrich Haas, staging by Claus Guth; 2022. Photo: Monika Rittershaus
Which productions have been noteworthy for you?
A work by Romeo Castellucci this year at the festival in Aix en Provence, Résurrection by Gustav Mahler, particularly struck me and once again stimulated me to think anew about what photography in the theatre is, and can be, for me. Described in very brief terms, Romeo Castellucci had an artificial mass grave dug at the Stadium de Vitrolles to Gustav Mahler’s Second Symphony. For me, this ‘theatrical installation’ was of incredible power and utmost relevance in our time. My question was: how can I bear to see this process and how can I translate it pictorially? It was extremely important for me to exchange ideas about this with Romeo Castellucci and his dramaturg Piersandra Di Matteo, and to look for a way to photograph.
The work on Bluthaus at the Bavarian State Opera with Claus Guth and his team, and the conversations with the wonderful leading actress Vera-Lotte Böcker, were significant for me also, because the crass subject matter of the piece was illuminated very sensitively, in all its facets. It is very nice to experience that a singer feels at ease in the awareness of my view of her during intensive rehearsals.
(ed. – The opera, by Georg Friedrich Haas, details the trauma of sexual abuse within one family; it was staged as part of Bayerische Staatsoper’s inaugural “Ja, Mai” festival in May 2022.)
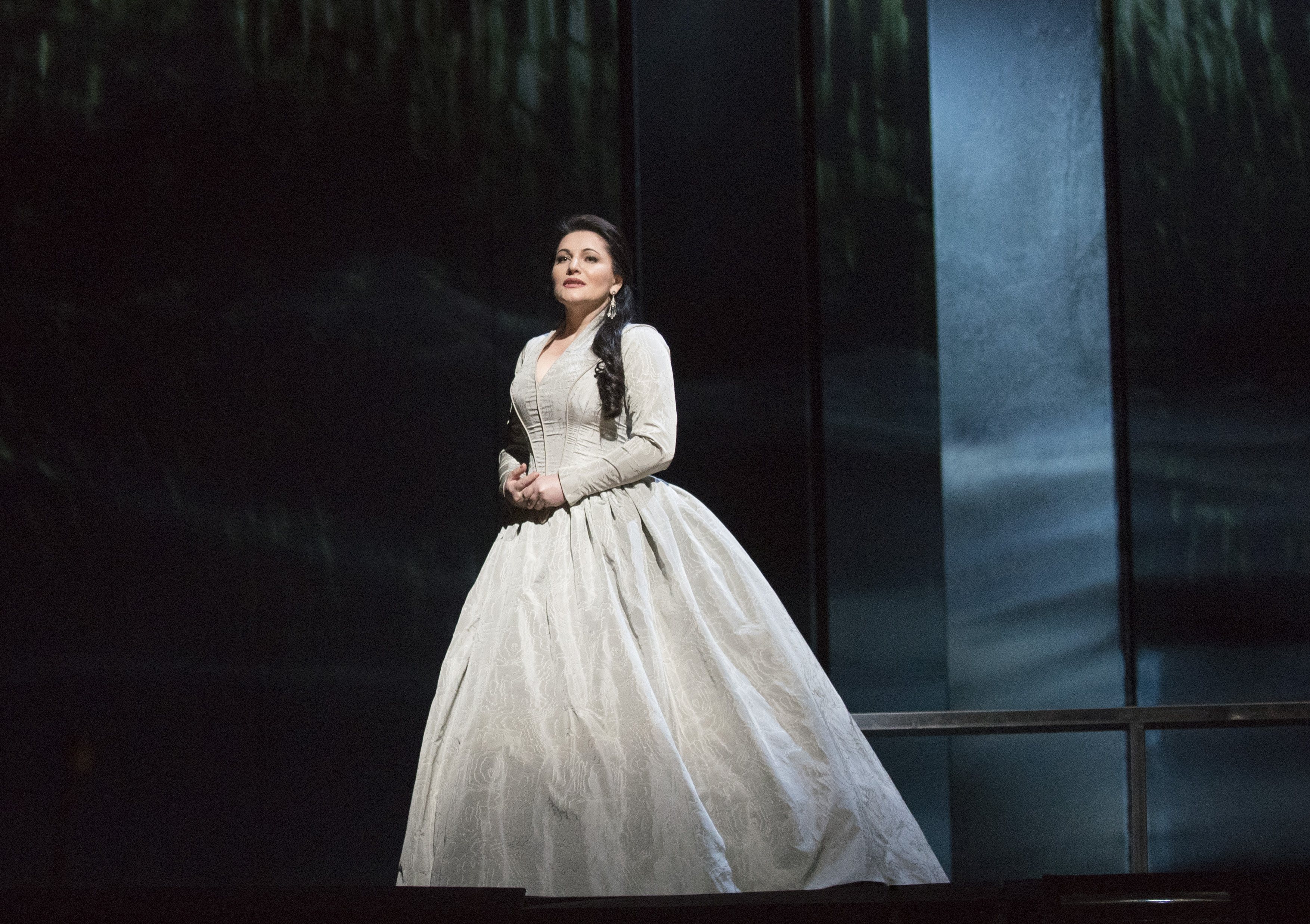
And: I would like to emphasize the continuous work at the Salzburg Festival – this year with three of “my” most important directors, Christof Loy (who staged Puccini’s Il Trittico), Barrie Kosky (Janáček’s Katja Kabanova) and Romeo Castellucci (a double-bill of Bluebeard’s Castle by Bela Bartók and De temporum fine comoedia (Play on the End of Time) by Carl Orff) – and three very strong singers: Asmik Grigorian (Trittico), Corinne Winters (Kabanova) and Ausrine Stundyte (Bluebeard/De Temporum).
Right now I’m having a very intense time with the Ring des Nibelungen with Dmitri Tcherniakov in Berlin. The four large pieces, in a very short time, were extremely challenging for all involved. Almost at the same time I photographed Die Walküre in Zürich, directed by Andreas Homoki. Photographing the same work in two completely different interpretations was a great pleasure for me.
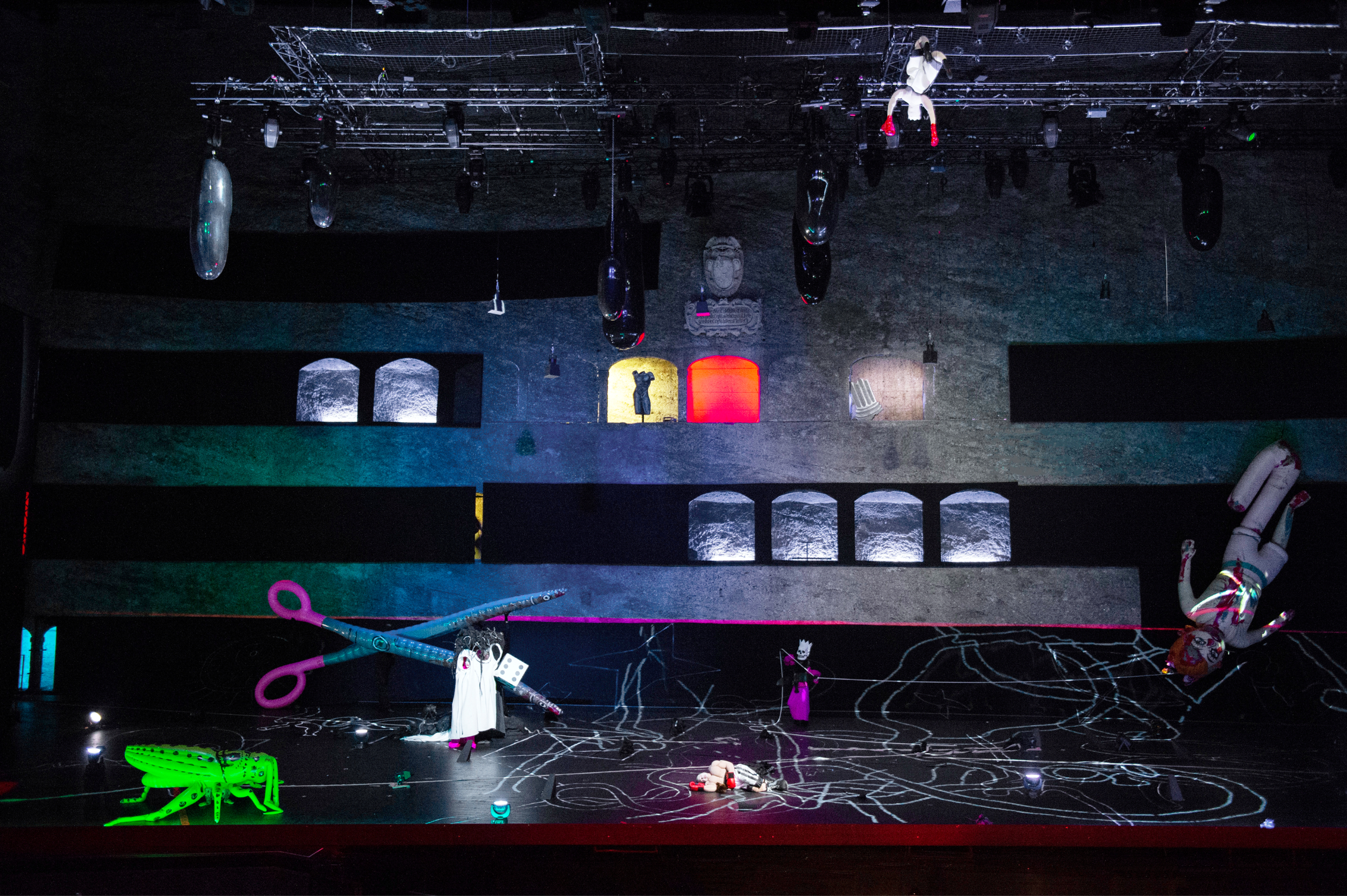

Christopher Maltman (c) as Oedipe in a scene from the Salzburg Festival staging of Enescu opera, by director Achim Freyer, 2019. Photo: Monika Rittershaus, part of The scene and the unseen (arnoldsche).
How did you choose the images in the book?
The scene and the unseen shows a selection of my favourite images of the productions most important to me. The sequence is purely pictorial, with the directors’ productions following one another because they are related in content and aesthetics. My desire was to celebrate the art form of opera.
As a stage photographer, my job is to translate the fleeting and complex three-dimensionality of a performance into a two-dimensional image. A photograph has its own time. It is through the calculated use of blur or blurring, or the unusual focus on minute details or peripheral events that I try to capture the mystery of a production.
To what extent do you think the public’s understanding of a production (or opera as an art form overall) has been expanded because of your work?
Whether the understanding of the public changes through my work, I cannot estimate – that would be presumptuous. I wish, of course, that I can bring to the spectators and viewers of my pictures the special qualities of opera performances, but whether this succeeds, I can not judge – only the others can do that.

Andreas Schager as Siegfried in a scene from Staatsoper Unter den Linden staging of Der Ring des Nibelungen: Götterdämmerung, by director Dmitri Tcherniakov; 2022. Photo: Monika Rittershaus








