“Powerhouse” is a term often used within the opera world, applicable to the artists performing on the stage as to much as to those creating off of it. In the case of André Barbe and Renaud Doucet, the term not only multiplies but broadens considerably. The creators of over forty new opera productions, the busy duo (and real-life couple) meticulously plan, design, direct, dramaturg, and offer their own precise, all-encompassing vision for works from French, Italian, German operatic and operetta repertoires. Their highly imaginative if deeply studious approach over the past two-plus decades has won them critical praise as well as legions of international fans.
Director and choreographer Renaud Doucet and set and costume designer André Barbe began their creative journeys in Quebec in the worlds of theatre, opera, dance, and television, before becoming a formal brand (‘Barbe and Doucet’) in 2000 and working as a team. Puccini, Rossini, Mozart, Massenet, Donizetti, Debussy, Offenbach, Berlioz, Bizet, Saint-Saëns, Fauré, Richard Strauss, Johann Strauss, and Dvořák – all composers whose works have enjoyed the Barbe and Doucet treatment, with stagings across famed houses including Staatsoper Hamburg, Opera de Toulouse, l’Opéra National du Rhin, l’Opéra de Marseille, Teatro La Fenice (Venice), Teatro Regio di Parma, Oper Köln, Volksoper Wien, Kungliga Operan (Stockholm), Opera Philadelphia, Seattle Opera, Vancouver Opera, and L’Opéra de Montréal, to name a few. In 2013 Barbe and Doucet staged critically-acclaimed production of Wagner’s first opera, Die Feen (The Faeries), for Oper Leipzig, a co-production with the Bayreuther Festspiel, marking the composer’s 200th birthday. Their colourful 2018 production of Saverio Mercadante’s Il Bravo for Wexford Festival Opera went on to win The Irish Times Theatre Award for Best Opera Production.
What’s especially notable about Barbe and Doucet is their ability to combine what might be termed the fun and the smart; their presentations offer a very complete vision of a very specific, occasionally identifiable world, or more often, multiple worlds. One’s imagination is engaged, often delighted, together with intellect; there is a seamless dance at work, and one barely notices until later contemplations – a head tilt; a bend of the collar; a slight pause between words. Nothing in the world of Barbe and Doucet is accidental. Both Die Feen and Il Bravo played with various levels of reality and perception, utilizing metadramatic situations and time shifts to highlight subtexts within respective librettos and scores, resulting in thoughtful if highly entertaining avenues of entry for newcomers. That instinct is especially noticeable in their 2019 production of Die Zauberflöte (The Magic Flute) for Glyndebourne Festival Opera wherein the historical figure of hotelier Anna Sacher was used as a foundation for a fascinating exploration of family, opportunity, independence, and intergenerational rifts – elements that were brought out with a zesty mix of whimsy and intelligence.
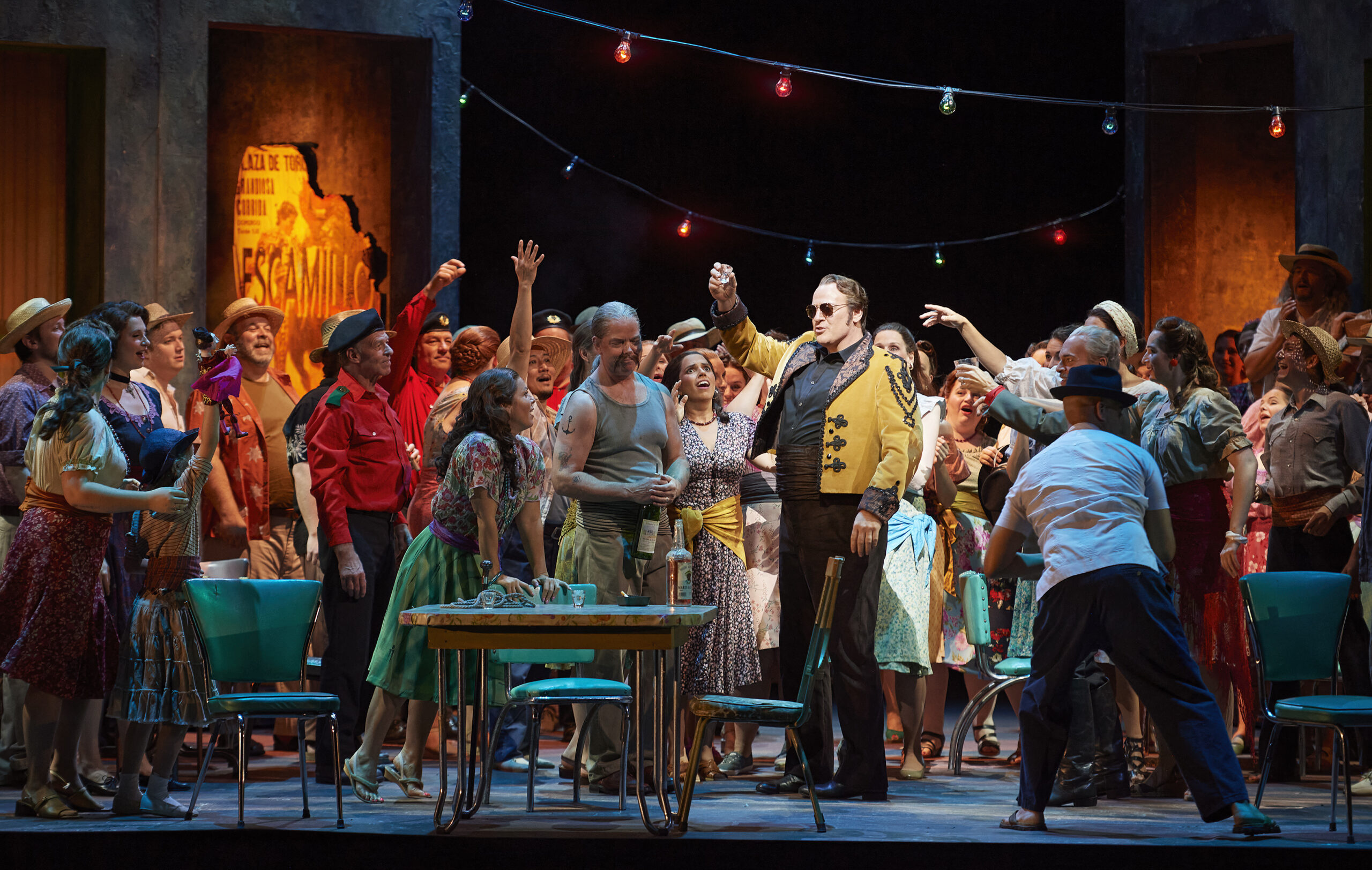
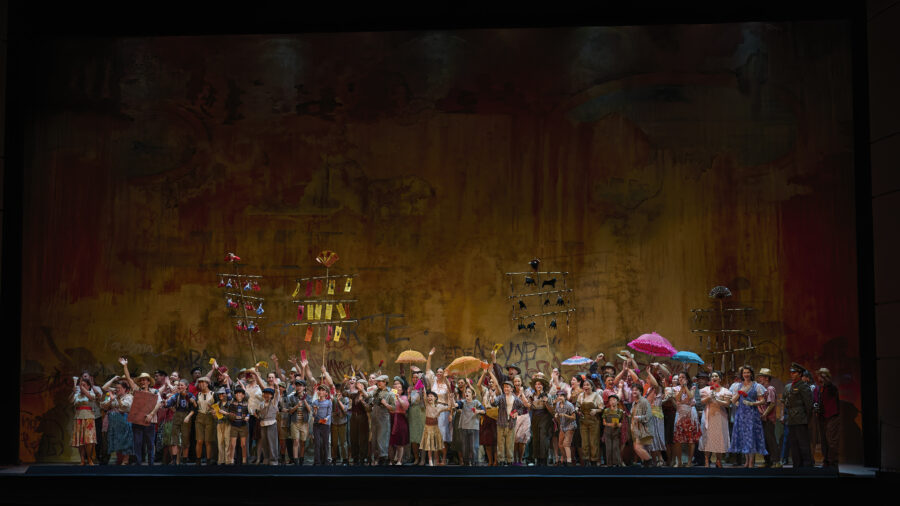
Those elements are equally noticeable in their 2014 staging of Donizetti’s Don Pasquale currently running now through May 18th in Toronto. First staged by Scottish Opera and presented earlier this year by Vancouver Opera, the presentation marks the duo’s company debut with the Canadian Opera Company (COC). The action of Donizetti’s 1843 opera is here presented in a vibrant and colourful 1960s Rome complete with leopard prints, a bold colour palette, and big bouffant hairdos. Pasquale runs a shabby terracotta-toned pensione overstuffed with knick-knacks, including a litany of lime-green, feline-shaped tchotchkes; the title character, in Barbe and Doucet’s staging, loves cats but can’t have any owing to pesky allergies. The opera’s plot-rich story – involving comical machinations by others who hope to gain control of his fortune – is presented with humour, pathos, and even tenderness, its designs a thoughtful reflection of Pasquale’s wartime-influenced ideas of abundance, and the inevitable ways those ideas bump up against a rapidly changing world.
Money was the very thing that opened our recent exchange, which took place in the pair’s dressing room a few days prior to Pasquale‘s official COC opening.
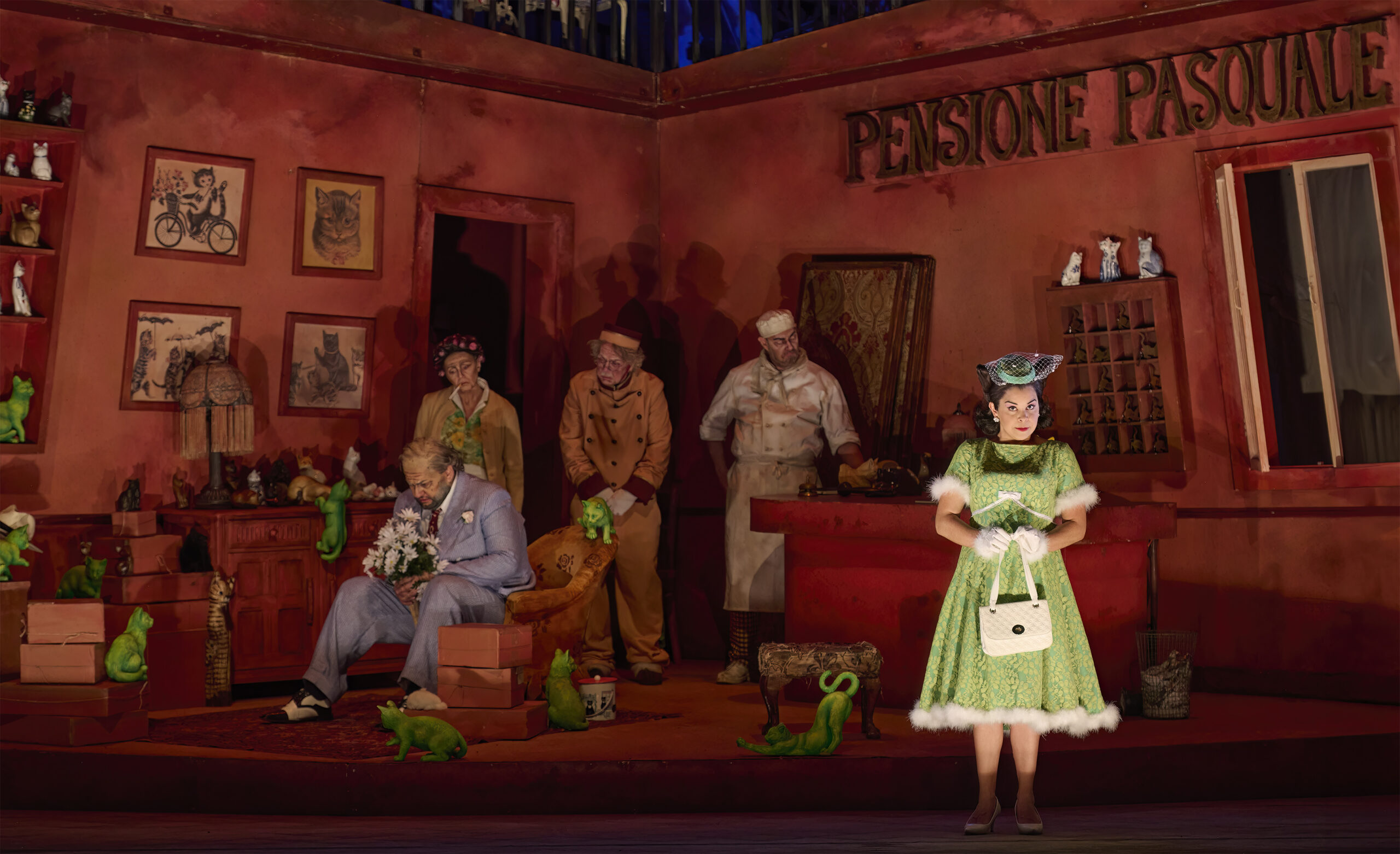

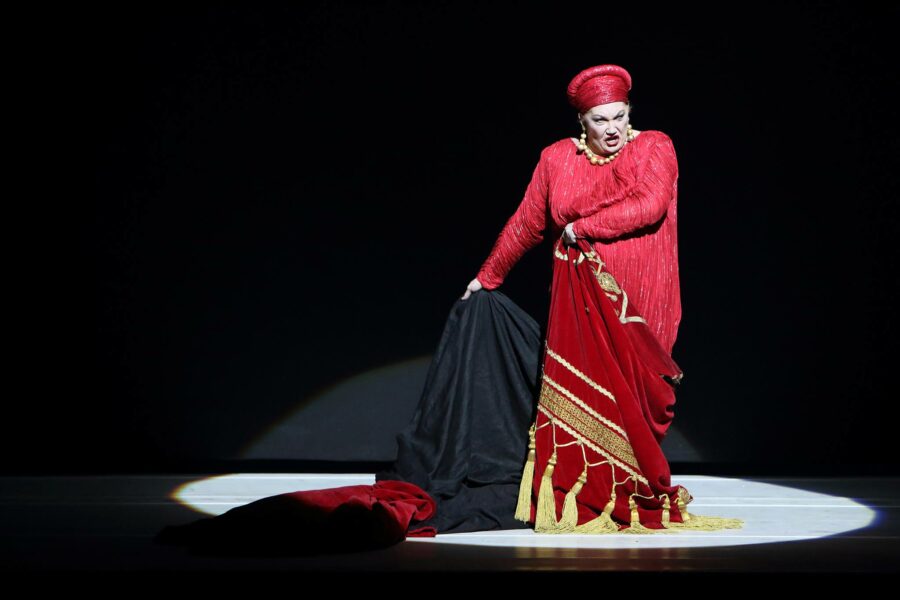
Misha Kiria as Don Pasquale (sitting) and Simone Osborne as Norina in the Canadian Opera Company’s production of Don Pasquale, 2024. Photo: Michael Cooper
Do budget cuts to opera mean changes to your work?
RD No it’s not that – companies will just cut new productions. There’s fewer of them that will actually be done.
AB When you look at big companies, it’s not that their budgets were always so enormous; it’s just that they had, and often do have, their own workshops. They can do their own thing. The companies have the manpower, yes, but it’s the supplies that have gone up: the price of lumber, the heating costs, the electricity costs; the war in Ukraine is a factor as well.
RD My first concern for the two of us is that we are working for the audience; we are working to reach an audience and making sure that when they leave the theatre they want to come back. I’m not not working for five critics; I’m not working for egos. When you have a theatre where the public come, where people are happy and they want to come back, this is the best publicity. But we’ve been through years of seeing performances where there were just 40 people in the audience, and oh my God, it was so fantastic – of course the opposite is also nice! When we did Die Feen in Leipzig – we were asked to do this production as a gift for Richard Wagner’s 200th anniversary; it was co-produced with Bayreuth – they said, “You know guys don’t be afraid and don’t be worried if there’s nobody.” And so we said, “Okay, well, we’ll do our best.” They were so surprised because the show wound up selling incredibly well – it was very popular. The same thing happened when we had shows in Hamburg – our shows there tend to sell out. There’s a reason for that.
Which is… ?
RD We work for the audience. This is the most important thing. It’s not so much about money as it is about time – people who dedicate themselves to what they do. The decision makers of the art form very often do not have a clue what the art form is about; boards don’t have a real clue about what we do; politicians certainly don’t have a clue about what we do and they never have. Companies hire most of the time, not all the time, but most of the time, people who are sometimes good with numbers and technology, but those are… objects. It’s about the audience.
Tall Poppies?

The Four Seasons Centre for the Performing Arts in Toronto. Photo: Lucia Graca
Why did it take so long for you to work with the Canadian Opera Company – especially since you’re Canadian?
RD I think a lot of people in the opera business do not know where to put us; we do not fit in a box.
AB Also we don’t live in Montreal now, and really, we’re not very social people. We are not the type of people who go spend their days schmoozing and trying to seduce. We’re mostly two like those two grumpy old guys (Statler and Waldorf) on The Muppet Show. Really, we are just two grumpy old guys who just want to do one thing: work.
RD Put me in a studio with singers; put André working on designs. We are both people who love to work. And we can be difficult people as well because we don’t take crap. Absolutely not.
So maybe a little bit of Tall Poppy Syndrome?
RD Yes, maybe. There is definitely a lot of that kind of thing in the opera world. I think also… I love something Speight Jenkins at Seattle Opera told us when we worked on Turandot: “For years I never wanted to hire you because everybody was telling me how problematic you are – you are not problematic, but you show instantly what the problems are and people who can and cannot solve them.” The issue – and he said this also – is that we need to work with people who know what they do well and are confident, which is why we work with the same companies, like Staatsoper Hamburg, for example Then there are companies who look at us like, “Oh my God, there are the two monsters.” But if I don’t direct things in a specific way people will say they cannot understand, so I’d rather be clear. When I create a new production that I create a (staging) score indicating every entrance, every intention, all the light cues, the exact placement of props – I give companies this information more than one year in advance, and they look at me and they say, “No, that can never happen with so many people.” And then they discover that, “Yes it can.” When we did a new Cenerentola at the Latvian National Opera, the company made a copy of our score for their National Library and said at the time, “We had never seen anything like this.”
AB We’re not doing all this for ourselves; everything we do, we do for the sake of the show.
RD If a singer arrives extremely prepared, there’s not going to be any improvisation because when the staging is known, it’s known. Sometimes colleagues will arrive at a house for rehearsals and say, “Okay, we’re doing this new production, let’s improvise and see what I want to take out of it.” If it works for them, that’s fine and bravo, but we’re not like this.
AB Every detail you see onstage has been discussed at home, every costume; every movement. We talk a lot about it beforehand.
RD Also we are hired to have a point of view on the production – mostly in Europe, that’s what they tell us: “If you do The Magic Flute, you have to have a point of view.” When we did it at Glyndebourne – Sebastian Schwarz was the Artistic Director at the time – we asked, “What do you want to do?” Because we’ve been asked many times to do this opera, and we always said no. We couldn’t say no to Glyndebourne of course, but we said, “What do you expect?” He said, “I would like to create a production where the grandparents come with their grandchildren and build memories.” Well, that’s a good start, isn’t it?
That production, with its references to Anna Sacher, Rosa Lewis, and the exclusive world of chefs, was staged in the early 20th century but felt incredibly current.
RD Well as you know from when we spoke about it before, some aspects of its score are problematic. When they asked us to do it, I said “Oh God, we’re going to have to deal with these things” and then they were telling us. “You know if you want to change the text or cut it out…” and I said no way, I would never dare to cut the text; I need to find solutions, not compromise. And this is a thing in this business which happens too often; that kind of compromise is a point when everybody loses. You give up a little, you give up a little more; we give up a little, then even more. That kind of compromise is not a good solution. We need to find creative solutions that work best within the parameters. And so we did.
AB Something similar happened when we worked with Scottish Opera. The budget was small, there were difficulties, and we offered the director, Alex Reedijk, the idea to build the costumes in Budapest, because we knew a shop over there that would save on costs. And he said, “No – the funding for this is from Scotland; I need to provide workers with jobs.” So again, we needed to find solutions within the existing parameters. We understood what was needed to build the production and we worked to make it happen.
RD He was, and still is, there to serve the people of Scotland – he knows that when the money is coming from the government, he needs to give jobs back to the people. It was a parameter that made me so willing to find solutions with them. It’s the teamwork that is so important. Opera is entirely about collaboration. We need to work together.
Precision & Freedom

Photo via IMG Artists
Is this why you place such importance on the rehearsal time?
RD Yes. When I work with (conductor) Jacques (Lacombe) it’s so fun; he’ll be the one giving the notes on the staging and I’ll be giving the musical notes. There’s a feeling we’re all working together.That’s why it’s very frustrating when you arrive in some rehearsals on the first day and you learn a singer has decided that they will come in three days or whatever, and releases are given to them. Some companies say, “Well, they know the role; they sang it before.” Yes, they know the music, but they don’t know the staging or maybe even the actual stage; they don’t know the intentions; they don’t know this exact world, in all senses. And you need to know these things in order to feel them.
We were doing Cenerentola in Toulouse (2024) and one of the singers had seen our staging of La bohème (2022) – she saw how precisely we were working, how every little thing is so detailed, and she said, “Oh my God, now I understand the amount of work that Bohème took! It looked so easy, so flawless” – but that’s the whole point, you work in rehearsals so that everything seems effortless. We rehearse breath, body, even a little movement of the finger – everything. So when that singer then arrives in front of the orchestra in the house they don’t have to worry about the staging because it is within their body, their muscle memory – they know precisely what to do, and they can concentrate on the music and on the conductor. They need to feel confident in the people around them, confident in the staging, confident in the maestro, confident in the monitors, confident in their dressers; confident that they can do their job to the best of their abilities.
Do you sense a sharpening divide in understandings with regards to the role theatre in opera presentation?
RD We have a problem now because many companies don’t want to hire opera directors; they want people from film, from television, from circus presentations. They don’t want to hire a real set designer who designs and knows about sets for the actual theatre either; they want to hire artists who don’t know about things like vanishing lines or scale. That’s okay if you want to try something new once in a while, but it’s a problem if you only rely on people who don’t know and understand theatre, and don’t read music and work mostly in film. When I’m staging a show, I read the orchestra score, I look at where the clarinet is placed, because then what is the sound compared to the voice? What is happening here? Then what is the space in which we hear this? We have four people here in this particular set piece so what is that about with this particular passage of music? Then you need to think, “Okay monitor here, monitor there” and “Be careful on this line, the soprano needs to take a support here” and “How do I bring her to do this difficult passage in the best condition?” and “How do I motivate that singer dramatically so that she doesn’t have to think about the special effect?” The thing I say to every singer, and I ask them not to crucify me before the end of my sentence, is, opera music does not exist in the production; you create the music. The music comes from you. I’m not sure all film directors understand this.
So would you say a more theatrical approach is needed now?
RD Yes. Singers will say, “Oh, here I’m singing legato here, and there I’m singing another way; that way it all gives a good effect.” And I say, think in terms of cause: what is the dramatic cause that creates the effect? And if you think in terms of cause and in terms of character, the effect comes naturally. That’s theatre. You can create specific sounds that creates specific emotions, but you take a point of view. Then after, you know, people like it or do not like it. It’s like food; I don’t want anybody to say it was not well cooked; you can say it’s not to your taste, but you can still know it’s been done well.
The Subtle Art Of Being Funny
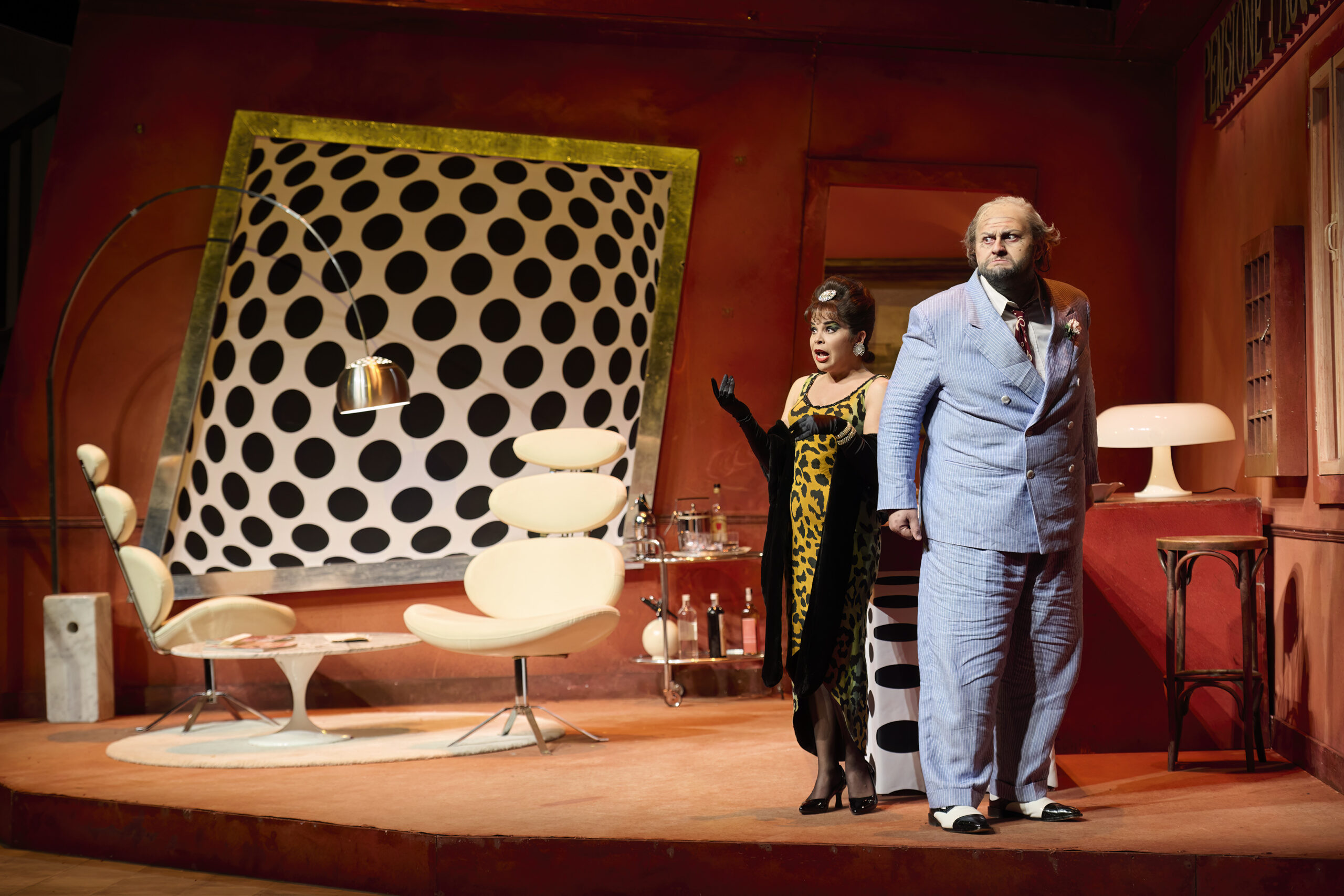

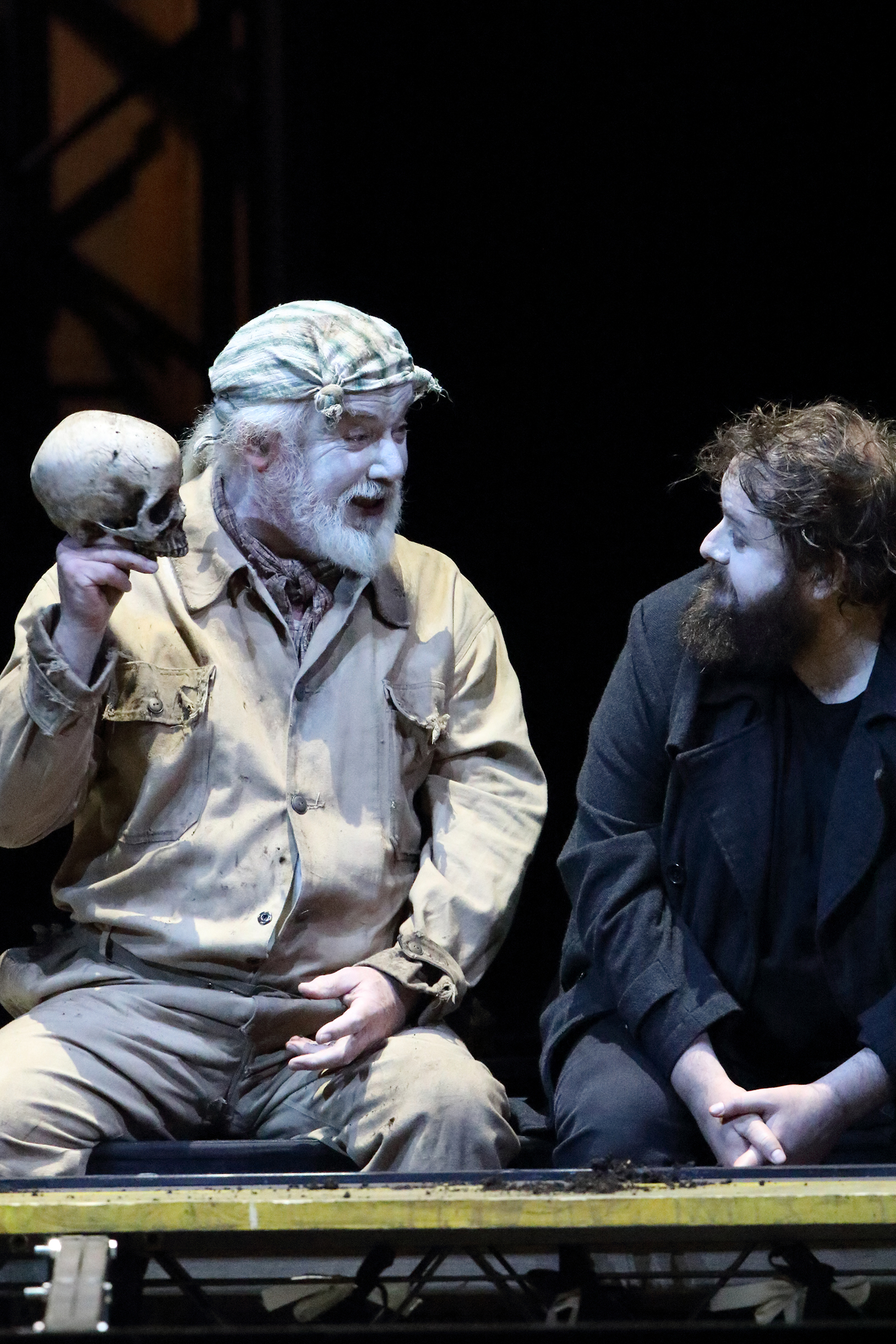
Simone Osborne as Norina and Misha Kiria as Don Pasquale in the Canadian Opera Company’s production of Don Pasquale, 2024. Photo: Michael Cooper
So how does your approach differ between operas like Don Pasquale and Pelléas et Mélisande, for instance – is it always the same process?
AB It’s always the same. Whatever the piece is we need to give it our full dedication – and comedies are sometimes much more difficult than drama; they demand an even greater level of precision.
RD Always be serious in comedy. Always. Some people arrive to rehearsals and say, “Oh, I’m playing a comedy so I’ll be funny now” And you know what? That’s not funny! You just have to be very sincere. And if you’re very true to the text and very sincere, the comic situation will happen by itself. To be sincere on stage means to be open, and that is difficult – it’s scary, but opening yourself is much easier if you can use a mask. When you have to be sincere in things like Pasquale, it’s very different, because there are moments where it’s really dramatic.
I’ve always felt Don Pasquale was this look into the lives of these four rather awful but very familiar people…
RD I don’t think they’re awful; I think they’re lovable!
Really?
RD For me it’s a conflict of generations; I think they don’t understand each other. The first thing I said to our Norina here (Simone Osborne) in rehearsals was, “Don’t be a bitch – you are not that; you have a goal and yes, things happen, but you need to know why they happen.”
So would you call it an opera buffa?
RD No, it’s not an opera buffa – Donizetti wrote it as a dramma giocoso; it’s written in the original score. There are some moments where you go, “Oh sh*t!” as well – it can be quite dramatic, and the people are sincere and lovable. You can understand, sometimes, why they do things and why sometimes they regret having done those things.
AB Also, you know, when you’re young and you see old people and you say,”Oh, they don’t understand anything.” And when you become old and you see young people and you say, “Oh, that’s not the way it used to be in my good old days” – this is something everybody experiences.
RD We all have an uncle who’s a Don Pasquale. He’s supposed to be a wealthy guy, but there’s different ways of being wealthy. What does it mean to have worth? To be rich? We set our production in Rome in the early 1960s and imagined that Pasquale (Misha Kiria) probably made money during WW2 on the black market. And he bought this little pensione and along the way got these odd jobs for people – the porter who was one of his friends; for the cook; for the maid – and they’ve been together for roughly 30 years. As a background story we also imagined that Pasquale is absolutely in love with cats – as you know there are cats everywhere in Rome – but he’s allergic to them, so this is why Dr. Malatesta (Joshua Hopkins) comes to treat him, although Pasquale is also a hoarder.
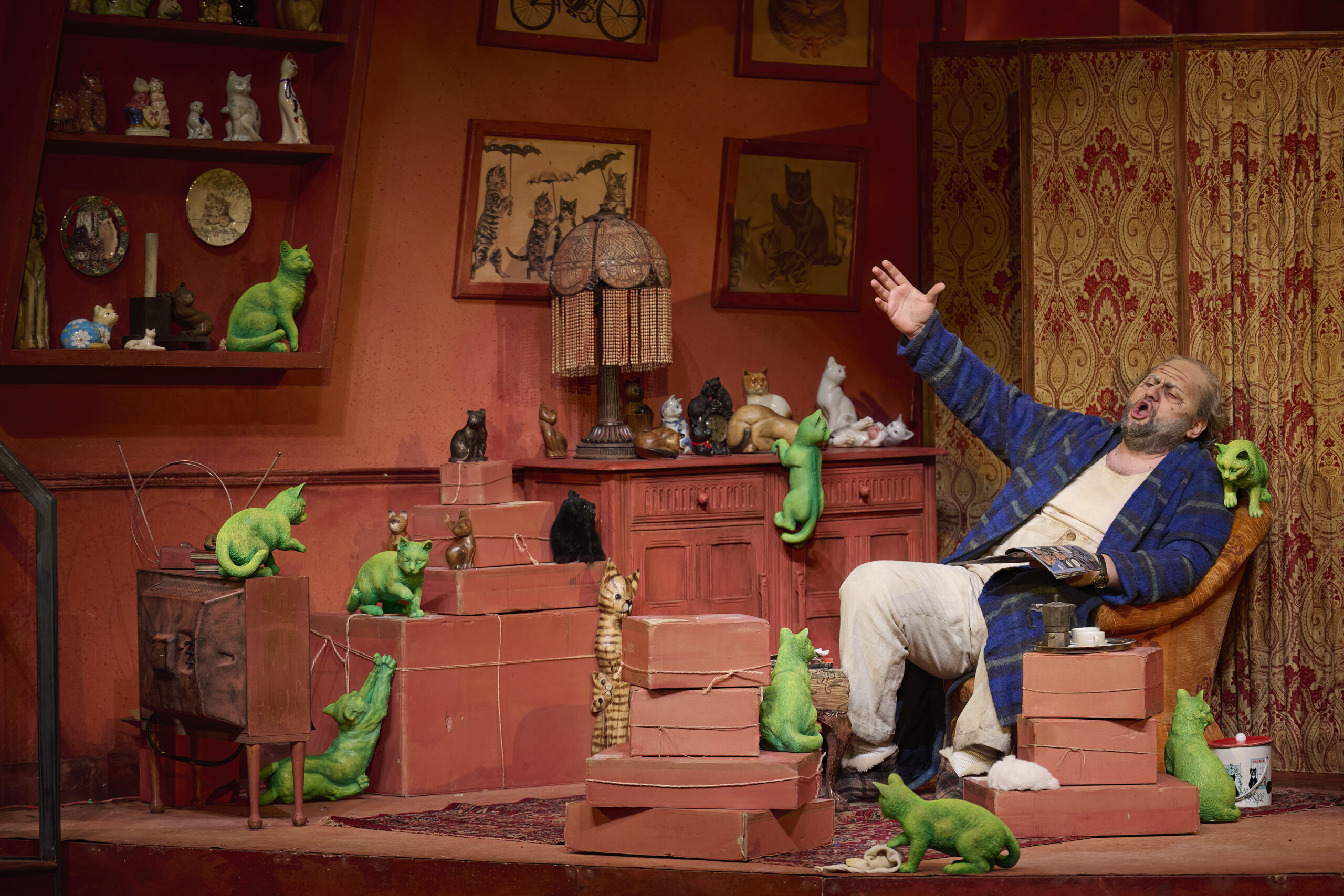

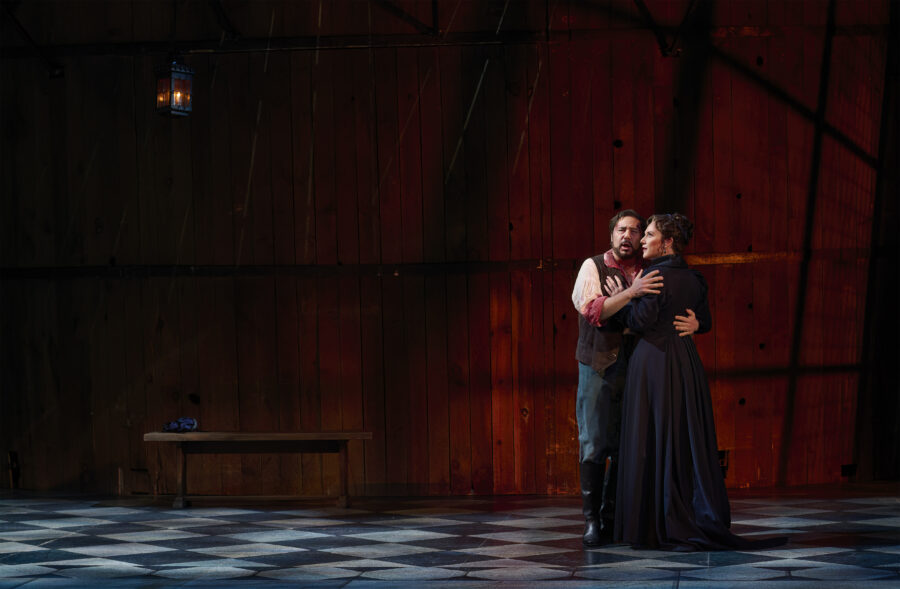
Misha Kiria as Don Pasquale in the Canadian Opera Company’s production of Don Pasquale, 2024. Photo: Michael Cooper
That’s a very clever subversion of the old “old single lady cat lady” cliché…
RD Yes, Pasquale is the cat gentleman! He’s also a hoarder, and he has money, but you’d never know from the way he lives. So when Sofronia spends his money, he’s panicking because she changed the furniture – but of course she did. What is actually really terrible for him is the change, that he’s being forced to break out of his old habits.
AB He’s an old guy and he wants to be in front of his TV, drinking coffee, and looking through his old issues of Cat Fancy magazine; he’s very happy that way. He likes the familiar comforts, it’s the familiarity, the predictability. But that’s what’s funny about this – we love to be in bed by nine o’clock too!
Early nights are wonderful…
RD They are wonderful. I’m not going to blame Pasquale, really – I don’t need anyone to come and change my habits either.
AB As I said, we’re the old guys from The Muppets!


















 Tori Wanzama is a new contributor. Her first opera was, in fact, my own introduction to the art form, at the age of four in what was then called the O’Keefe Centre in Toronto. It’s a bit too easy to close ears and heart to something that’s sat in one’s consciousness for so very long, and which is also a tremendous part of the cultural milieu; it is just as much of a challenge to re-open one’s mind to such a relentlessly (brilliantly) melodic work when one is constantly surrounded (by choice as much as necessity) by things so unlike it. And yet, Tori’s enthusiasm and creative insight all work together here to provide fresh, new ground – for me, as much as for those who feel too deeply rooted in classical cynicism. What can possibly grow in such highly acidified soil, after all? Tori’s writing gives opera newbies a bit of needed encouragement toward exploring an art form they (as she rightly outlines) might have their own preconceptions about, and also gives old cynics (alas) a new breath of the curiosity that felt so important to these pursuits in the first place. Reading her words was akin to seeing an old friend after many decades; all the old animosities simply departed. Tori is a second-year Communications student and has, as you will read, an incredible talent for the observation of stagecraft, as well as the nature of opera fandom itself. I look forward to publishing more of her work here in future.
Tori Wanzama is a new contributor. Her first opera was, in fact, my own introduction to the art form, at the age of four in what was then called the O’Keefe Centre in Toronto. It’s a bit too easy to close ears and heart to something that’s sat in one’s consciousness for so very long, and which is also a tremendous part of the cultural milieu; it is just as much of a challenge to re-open one’s mind to such a relentlessly (brilliantly) melodic work when one is constantly surrounded (by choice as much as necessity) by things so unlike it. And yet, Tori’s enthusiasm and creative insight all work together here to provide fresh, new ground – for me, as much as for those who feel too deeply rooted in classical cynicism. What can possibly grow in such highly acidified soil, after all? Tori’s writing gives opera newbies a bit of needed encouragement toward exploring an art form they (as she rightly outlines) might have their own preconceptions about, and also gives old cynics (alas) a new breath of the curiosity that felt so important to these pursuits in the first place. Reading her words was akin to seeing an old friend after many decades; all the old animosities simply departed. Tori is a second-year Communications student and has, as you will read, an incredible talent for the observation of stagecraft, as well as the nature of opera fandom itself. I look forward to publishing more of her work here in future.






